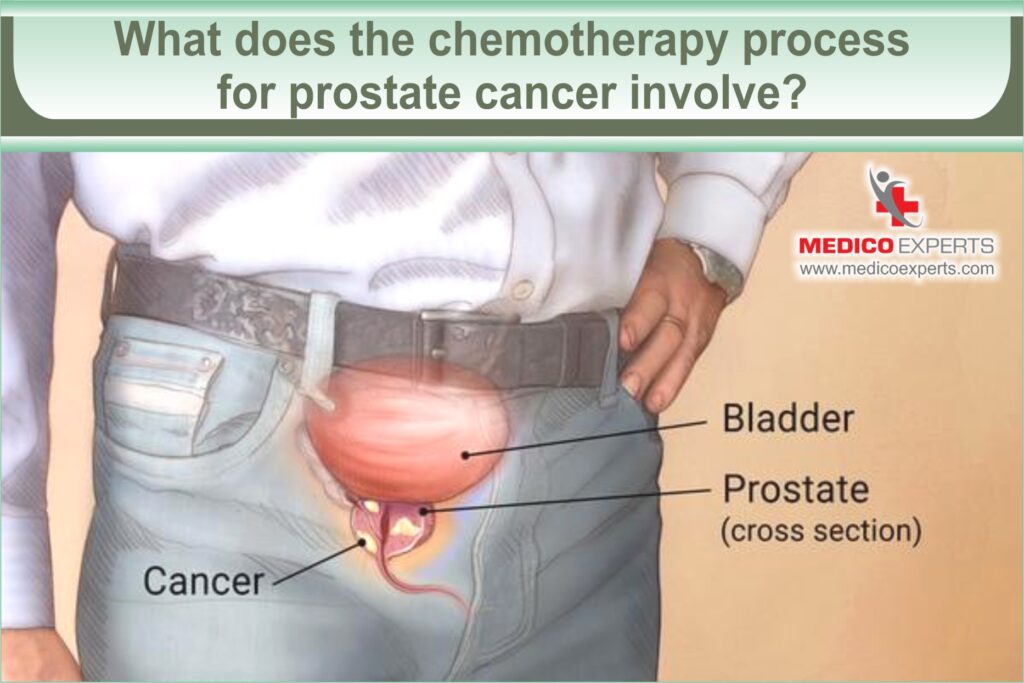
Curious about Acute Leukemia in adults? Dive into our blog where medical insights meet individual resilience.
Ever found yourself lost in the intricate world of medical jargon, curious about learning the impact adults face with Acute Leukemia?
Let us walk you through the complicated subject of acute leukemia in adults – a condition that demands your attention and understanding.
As we go further, you’ll not only grasp the essentials of acute leukemia in adults but also discover insights that can shape how you face it.
So, let’s quickly dive in…
As per research published in Blood Cancer Journal, about 80% of all acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) cases occur in children; however, when the disease is detected in adults, it can pose a significant threat.
Cancer develops when cells in the body start multiplying uncontrollably. There are several types of cancer. The development of cancerous cells is possible in virtually every part of the body.
Let us go ahead and understand basic to advanced concepts associated with acute leukemia in adults.
What Is Leukemias?
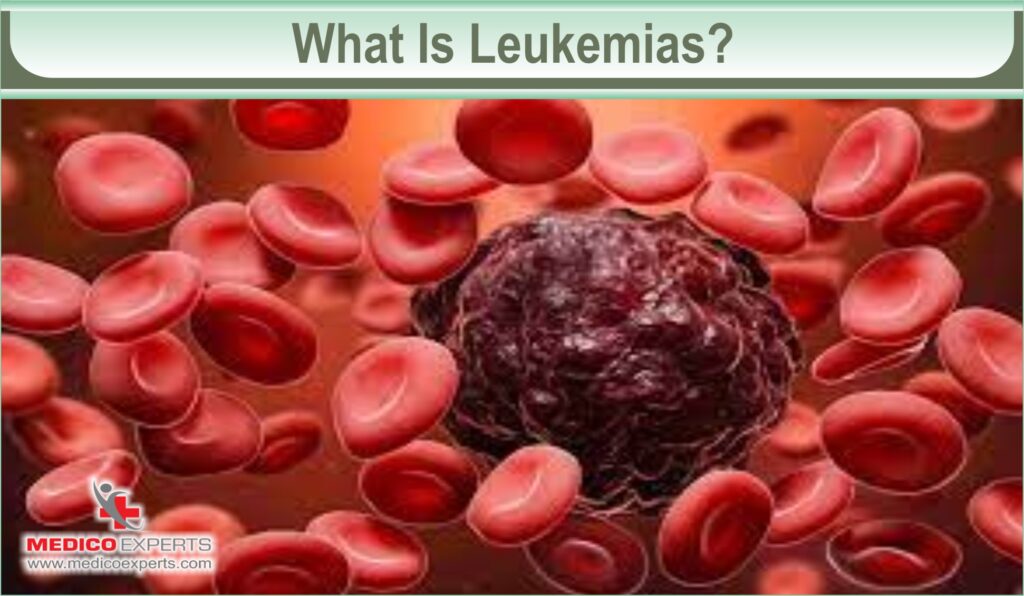
Leukemias are tumors that begin in cells that ordinarily mature into several types of blood cells. Most leukemias begin in the early stages of white blood cells, although others begin in other types of blood cells.
There are various forms of leukemia, which are distinguished primarily by whether the leukemia is acute (rapidly developing) or chronic (slowly growing), as well as whether it begins in myeloid or lymphoid cells.
Knowing the kind of leukemia helps experts anticipate each patient’s outlook and choose the appropriate treatment.
Learn more about leukemia types and cures.
What is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia in Adults?
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), is a form of cancer that affects both the blood and the bone marrow, which is the spongy tissue found inside bones and is responsible for the production of blood cells.
As a result of the rapid progression of the disease and the production of immature blood cells rather than mature ones, the term “acute” is used to describe acute lymphocytic leukemia. When referring to acute lymphocytic leukemia, the term “lymphocytic” specifically refers to the white blood cells known as lymphocytes, which are affected by ALL.
An alternative name for acute lymphocytic leukemia is acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
The most prevalent form of cancer in children is acute lymphocytic leukemia, and the therapies that are available for this disease result in a good likelihood of curing it. Adults can also be diagnosed with acute lymphocytic leukemia; however, the likelihood of a cure is significantly lower.
What are the Symptoms of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia in Adults?
Each person may have different signs of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia. Among the most common symptoms are:
Bleeding from the Gums:
Unusual bleeding that starts in the gums, potentially indicating disruptions in the blood clotting process.
Bone Pain:
Aching or discomfort in the bones, suggests the impact of leukemia on the bone marrow where blood cells are produced.
Fever:
Persistent or recurring high body temperature is a common response to the body fighting against abnormal cell growth.
Frequent Infections:
Repeated or persistent infections reflect the compromised immune system due to the prevalence of immature blood cells.
Frequent or Severe Nosebleeds:
Nosebleeds that occur frequently or are unusually severe are indicative of potential issues with blood clotting.
Lumps Caused by Swollen Lymph Nodes:
Noticeable lumps in the neck, armpits, abdomen, or groin areas, resulting from swollen lymph nodes reacting to abnormal cell activity.
Pale Skin:
Unusual paleness of the skin, a sign of anemia caused by a shortage of healthy red blood cells.
Shortness of Breath:
Difficulty in breathing is potentially linked to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity due to a decrease in red blood cells.
Weakness, Fatigue, or General Decrease in Energy:
Overwhelming tiredness, weakness, or a notable decline in overall energy levels is often associated with the body’s struggle against leukemia’s impact on normal blood cell production.
Night Sweats:
The amount and warmth of sweat can help you figure out if night sweats are linked to leukemia or other blood cancers.
You may have severe night sweats, even in a cold environment, and wake up soaked in perspiration and this could be a sign of leukemia as per the study shown by Leukaemia Care.
These symptoms collectively provide a glimpse into the detailed challenges that individuals with acute lymphocytic leukemia may face.
What are the causes of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia?
The development of mutation in the genetic material or DNA of a bone marrow cell is that which leads to the development of acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Normal DNA Function:
DNA tells cells how to make proteins and other chemicals that are necessary for their structure and function. This is done by DNA, it guides a cell’s development and lifespan, ensuring it grows at a predetermined rate and dies at a predetermined time.
Aberrations in DNA:
Mutations provide a signal to bone marrow cells, telling them to continue uncontrolled development and division, which disrupts the usual programming of cell survival cycles.
Uncontrolled Blood Cell Production:
The above function causes a crazy increase in the number of blood cells being made. Immature cells are the primary occurrence in the bone marrow, where they change into lymphoblasts, which are white blood cells that are linked to leukemia.
Malfunctioning Lymphoblasts:
These abnormal lymphoblasts deviate from normal operations. They not only fail to function properly but also have the potential to accumulate, making it challenging for the body to distinguish between healthy and abnormal cells.
Complex Origins of DNA Alterations:
We are still not sure where the DNA changes that cause acute lymphocytic leukemia come from. The intricate interplay of factors contributing to these mutations remains a subject of ongoing research.
There is a lack of comprehensive understanding of the origin of the illness, which is the DNA abnormalities that might lead to acute lymphocytic leukemia.
How is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Diagnosed?
When it comes to identifying and understanding Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL), a comprehensive approach is taken through a series of diagnostic procedures.
This process begins as follows:
Blood Tests:
Blood tests are done to unveil abnormalities in blood cell counts.
Too many or too few white blood cells, inadequate red blood cells, low platelet count, and the presence of blast cells—immature cells typically found in the bone marrow.
Bone Marrow Test (Aspiration and Biopsy):
A needle extracts a sample of bone marrow from the hipbone or breastbone.
The lab scrutinizes the sample to identify leukemia cells.Doctors classify blood cells based on size, shape, genetic features, and molecular characteristics. This helps in determining the type of leukemia and developing a tailored treatment plan.
Imaging Tests:
To assess the extent of cancer spread certain tests are performed to understand the depth of the cancer spread.
Doctors use X-rays, computerized tomography (CT) scans, or ultrasound scans to look at different parts of the body, such as the brain, spinal cord, or other body parts.
Spinal Fluid Test (Lumbar Puncture):
Involves collecting spinal fluid through a lumbar puncture or spinal tap.
To examine whether cancer cells have infiltrated the spinal fluid, providing insights into the potential spread of leukemia.
What are the risk factors linked with acute lymphocytic leukemia?
Adults, who have undergone certain types of chemotherapy and radiation therapy for previous cancer treatments may face an increased risk of developing acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Exposure to Radiation:
People exposed to exceptionally high levels of radiation, such as survivors of a nuclear reactor accident, are at an elevated risk of developing acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Genetic Disorders:
Certain genetic disorders, like Down syndrome, are linked to an increased susceptibility to acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Support and Information:
MedicoExpert’s Tumor Board provides comprehensive care for acute lymphocytic leukemia. The team brings together a group of experienced health professionals, with each adding their unique perspective to make sure you get the best care possible.
The MedicoExperts’s Tumor Board is committed to empowering you with more power by offering insights beginning with the diagnosis and continuing through treatment and beyond.
Associated Procedures:
Medicoexpert offers various associated procedures for acute lymphocytic leukemia diagnosis and treatment, including bone marrow biopsy, bone marrow transplant, and chemotherapy.
Understanding these risk factors and seeking support from reputable medical platforms helps navigate the challenges associated with acute lymphocytic leukemia.
What are the Treatment options for Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia?
The journey of treating Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL) in adults involves a strategic plan divided into distinct phases, each playing a crucial role in battling this blood cancer.
It has been reported by the National Cancer Institute that there are a number of different therapy options available.
Let us see them in detail:
Chemotherapy:
The use of drugs to eliminate cancer cells. It is a cornerstone in the induction therapy and may also be employed during consolidation and maintenance phases.
Targeted Therapy:
Targeting specific abnormalities within cancer cells, this treatment prompts the death of cancer cells. It can be used alone or combined with chemotherapy in various treatment phases.
Radiation Therapy:
High-powered beams, such as X-rays or protons, are utilized to destroy cancer cells. If the cancer spreads to the central nervous system, radiation therapy may be recommended.
Bone Marrow Transplant:
It involves replacing leukemic bone marrow with leukemia-free marrow from a compatible donor. It is utilized in consolidation therapy or for treating relapse.
CAR-T Cell Therapy:
A cutting-edge treatment engineering germ-fighting T cells to combat cancer. This might be an option, especially for children and young adults, in consolidation therapy or relapse treatment.
Clinical Trials:
In clinical trials, new medicines and standard treatments are being tested. While uncertain, they provide an opportunity for the latest advancements. Discussing benefits and risks with the doctor is crucial.
Additional Treatment Therapy:
Some of the additional treatment therapies are as follows:
Induction Therapy:
The initial phase aims to eliminate the majority of leukemia cells in the blood and bone marrow while restoring normal blood cell production.
Consolidation Therapy (Post-Remission):
Targeting any remaining leukemia cells, this phase intensifies the assault to ensure complete eradication of the disease from the body.
Maintenance Therapy:
This extended phase focuses on preventing the resurgence of leukemia cells. Treatment during this stage involves lower doses administered over an extended period, often spanning years.
Spinal Cord Preventive Treatment:
Throughout the treatment phases, additional measures are taken to eliminate leukemia cells in the central nervous system. Chemotherapy drugs may be injected directly into the spinal fluid as part of this preventive approach.
What are the chances of survival of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)?
Your doctor utilizes information derived from various tests and procedures to evaluate your prognosis and formulate suitable treatment options.
Unlike some other cancers that utilize numerical stages to indicate the extent of spread, acute lymphocytic leukemia doesn’t follow such staging.
Instead, the severity of your condition is assessed based on:
- The type of lymphocytes implicated, distinguishing between B cells and T cells. (B cells – B cells make antibodies that fight germs and viruses. T cells – Link and activate the immune cells that help to regulate responses from the immune system.)
- The specific genetic alterations present in your leukemia cells.
- Your age.
- Findings from laboratory tests, including the count of white blood cells identified in a blood sample.
The treatment duration for Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia can extend from two to three years, tailored to the individual’s situation.
Considering individuals aged 65 and older, complications from treatments tend to be more prevalent.
It is advisable to have a comprehensive discussion with your doctor, weighing your overall health, personal goals, and preferences.
Conclusion:
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) can happen to anyone, but kids and teens are more likely to get it. It is a kind of cancer that affects both the bone marrow and the blood. The rate at which this particular form of cancer spreads is fairly rapid. But patients with ALL are living longer now since there are better treatment options.
A patient’s life with ALL, even if it’s treated is still hard in some ways. But in this journey, having a reliable source of guidance and expertise becomes paramount.
MedicoExpert’s Tumor Board stands as a support. Comprising a team of medical professionals, this platform provides personalized insights and collaborative strategies for managing Acute Leukemia in Adults.
The Tumor Board brings together specialists from various fields, fostering a comprehensive approach to treatment decisions. This collaborative effort ensures that individuals facing Acute Leukemia receive tailored, evidence-based recommendations, empowering them to make informed choices about their health.
Your journey with Acute Leukemia will differ for each individual, and MedicoExpert is here to assist you at every step. Whether you seek guidance, a second opinion, or a comprehensive treatment plan, our Tumor Board is ready to support you. Allow us to guide you by booking an appointment.