Prostate Cancer Treatment In India With Cutting-Edge Technologies With Highest Success Rates
Prostate cancer is the 4th most prevalent cancer in the world, with 1.41 million cases according to the WHO. Typically, it occurs in old age and may not show any signs or symptoms in its early stages.
Detection of cancer itself is a matter of grave concern. However, with the advancement of technologies both in detection and treatment, the survival rates are also increasing.
Let me introduce you to one of our patients, Daniel Banda from Ibadan, Nigeria. Daniel has benefited from prostate cancer treatment in India.

It is a type of cancer that affects the prostate.
The prostate is a small, nut-shaped gland in males that produces the seminal fluid that feeds and carries the semen.
It is one of the more prevalent types of cancer. Many prostate cancers develop slowly and limit themselves to the prostate gland, where they may not cause severe damage. However, in some cases, it becomes aggressive and spreads quickly to other neighboring body parts.
Prostate cancer in its initial stages, confined to the prostate gland, and the patient has the best chance of success with minimal treatment and complications.
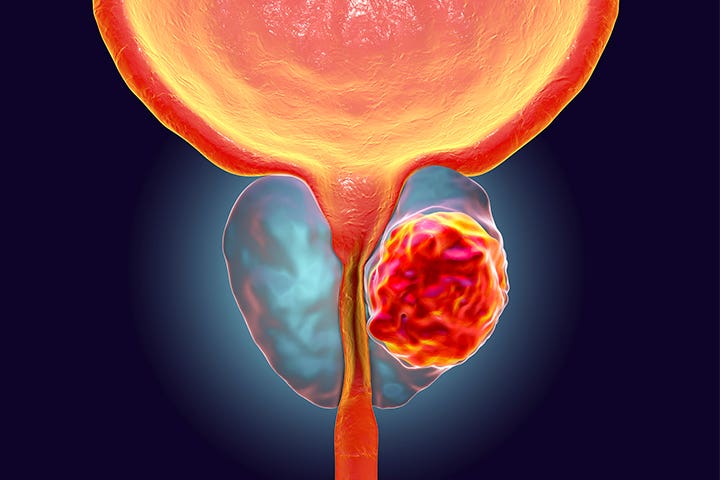
After the diagnosis of cancer of the prostate gland, the doctor will try to figure out the spread of cancer, which is known as staging. The stage of it refers to the spread of cancer in the body. Your treatment plan also depends upon the stage of prostate cancer.
Before we begin with the staging, let’s understand a few terminologies
The most widely used staging system for prostate cancer is the AJCC (American Joint Committee on Cancer) TNM (tumor (T), nodes (N), and metastases (M)) system.
The Grade Group (based on the Gleason score) indicates how quickly the cancer is likely to grow and spread. The results of the prostate biopsy determine this (or surgery).
It is classified into four stages: I, II, III, and IV. Some stages are further divided (A, B, etc). The lower the number, the less cancer has spread in general. A higher number, such as stage IV, indicates that cancer has progressed further.
Stage 1
Prostate cancer is growing, but it hasn’t spread beyond it.
In most cases, the doctor won’t be able to feel or see the tumor during a DRE or imaging tests.
The tumor covers half of one side of the prostate or less.
- The PSA level is less than 10
- The Gleason score is 6 or less
Stage 2A
The prostate cancer is growing, but it hasn’t spread beyond it.
During a DRE, the doctor might or might not be able to feel the tumor or see it on an imaging test. The tumor can affect more than half of one of the prostate’s lobes but not both.
- The PSA level is less than 20
- The Gleason score is 7 or less
Stage 2B
The prostate cancer is growing, but it hasn’t spread beyond it.
During a DRE, the doctor might or might not be able to feel the tumor or see it on an imaging test. The tumor can be found in one or both of the prostate’s lobes.
- The PSA level is less than 20
- The Gleason score is 7
Stage 2C
The cancer hasn’t spread beyond the prostate. During a DRE, the doctor might or might not be able to feel the tumour or see it on an imaging test. The tumor can be found in one or both of the prostate’s lobes.
- The PSA level is less than 20
- The Gleason score is 7 or 8
In comparison to stage IIB, the cancer cells appear to be more abnormal.
Stage 3A
The cancer hasn’t spread outside the prostate. During a DRE, the doctor might or might not be able to feel the tumor or see it on an imaging test. No lymph nodes have been affected by the cancer.
- The PSA level is at least 20
- The Gleason score is 8 or less
Stage 3B
The cancer has spread outside the prostate, but it hasn’t reached the lymph nodes or other distant parts of the body.
- The PSA is at any level
- The Gleason score is 8 or less
Stage 3C
The cancer may or may not have spread outside the prostate. No lymph nodes have been affected by the cancer.
- The PSA is any level
- The Gleason score is 9 or 10
Stage 4A
The cancer may or may not have spread to tissues near the prostate. Although the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, it has not spread to other parts of the body.
- The PSA is any value
- The Gleason score is any value
Stage 4B
The cancer may or may not have spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes. The cancer has spread to other parts of the body, including lymph nodes, bones, and organs.
- The PSA is any value
- The Gleason score is any value
Its staging is a bit complex. Your oncologist is the best person to conclude what is the stage of your cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. At what age does prostate cancer occur?
Prostate cancer is rare among men under the age of 40, but the probability of having prostate cancer increases rapidly after the age of 50. About 6 in 10 men over the age of 65 have prostate cancer.
2. What is the best fruit for the prostate?
Strawberries, blueberries, raspberries and mulberries are recommended for an expanded prostate diet. The prostate is controlled with potent hormones called sex hormones, including testosterone.
3. Is a PSA of 6.5 Bad?
PSA concentrations lower than 4 ng/ml are generally considered normal, while concentrations higher than 4 ng/ml are considered abnormal.
PSA levels of 4 to 10 ng/ml indicate a higher-than-normal risk of prostate cancer. When PSA levels are more than 10 ng/ml, the risk of prostate cancer is much higher.
4. How long do you normally live with prostate cancer?
Nearly 100 percent of men with local or regional prostate cancer will survive more than five years after diagnosis. Few men (approximately 7%) have more advanced prostate cancer when diagnosed.
5. Can prostate cancer make itself go away?
Simply put, yes, prostate cancer can be cured when it is detected and treated quickly. The vast majority of prostate cancer cases (over 90%) are discovered early, making tumors more susceptible to response to prostate cancer treatment.
Next in Prostate Cancer

Author Bio:
Dr. Yashashree Joshi – MBBS, MD (Philippines)
Dr. Yashashree Joshi, MD, is a globally-trained oncologist with a robust academic background and extensive experience in pioneering cancer treatments. Dedicated to patient-centered care, she continually integrates the latest advancements in oncology to provide her patients with innovative and personalized treatment plans.
Content Medically Reviewed By MedicoExperts Editorial & Clinically Review Board




