Organ transplantation in India is saving lives of patients across the globe
How chronic kidney disease leads to kidney failure?
Dialysis is not the cure for kidney failure. The only effective treatment for kidney failure is kidney transplantation.
The results of organ transplantation in India, including kidney transplantation, are as good as in any other developed country.
Let’s share the experience of one of our patients.
Samuel is a 52-year-old owner of a tour and travel company in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. He has been running his business for the past 25 years. He has a pretty wife and two kids, both of them studying in the USA.
Samuel’s dream is to become a very successful businessman in his country, and he wanted to have a long vacation in Europe with his wife.
Samuel was so busy in his business that he compromised his health and worked for hours without caring for his health. He also had the bad habits of smoking and drinking alcohol. One day when he was getting ready for his work, he fainted. His wife Laura called their family doctor for a checkup. The doctor advised Laura to have a full-body health checkup to find out the root cause.
The next day Samuel went to the hospital to have the checkup done.
Reports came, and his creatinine level was 6, which indicates severe kidney damage. The doctor suggested him for weekly dialysis and medication.
After a few years, the decline of kidney function was gradual but continual. His wife, Laura, had seen this decline first-hand, was heartbroken to watch her husband suffer, and was willing to do anything possible to save her life.
One of the most visible signs of Samual’s illness was the swelling of his limbs that affects many patients with kidney disease.
Samuel was getting his dialysis done regularly, but he knew that a kidney transplant was his best option for recovery, as his kidney functioning had reduced at three percent.

His research understood that dialysis was only a supportive therapy for kidney disease symptoms and not a cure for the disease itself. Without a transplant, dialysis must be done a few times each week for life.
To save the life of Samuel both of his sons were willing to donate their kidneys to his father. They both were very informative and brave. They did HLA match testing, and the elder child’s kidney was declared suitable for transplant.
Samuel’s wife Laura had done very well research on kidney transplantation options in different countries. Her sons checked in the USA, and she also explored India, Thailand, and Singapore. Being an educated family, their concern was to create a perfect balance in the success rate and affordable cost. During that stage, she got in touch with MedicoExperts, and the team helped her to make the right and informed decision.
They eventually selected India to conduct the transplantation. MedicoExperts patient care executive helped her further to zero down the doctor and hospital as per her budgets and concerns. The family consulted with three doctors, one from Delhi, One from Mumbai, and one from Bangalore, sitting there in Addis.
After a few weeks of the decision, all the documentation work was done, and she traveled to India with her husband and elder son.
Samuels got admitted, an evaluation was performed, and finally, the transplant day came after all the paperwork in India. Laura was in a deep panic as her two important family members were being prepared for the surgery.
She was absolutely relieved listening to the news that the surgery was successful and both his son and husband were fine. Samuel was given anti-rejection injections after the surgery. The doctors and their team took good care and monitored the progress very diligently.
After three weeks, Samuel got discharged. The doctor had asked him to stay in India for one more month to monitor Samuel’s progress. Laura was very happy with the whole process.
After four months, Samuel was back in his rhythm without any tiredness and weakness. No dialysis anymore.
There are many case studies of so many patients where families got a second lease of life with skillful surgeries and favorable outcomes.
Now let’s understand in detail about organ transplants.
Organ Transplantation is a medical procedure in which a failing or damaged organ is removed from a patient’s body and replaced with a functioning one. The donated organ may be from a living donor or a cadaver donor.
Organs that have been successfully transplanted include the heart, kidneys, brain, lungs, pancreas, intestine, and thymus. Organ transplantation is often the only treatment for end-stage organ failures, such as kidney failure, liver, and heart failure.
Organ transplantation is often lifesaving and gives the recipient a wonderful new lease of life. It is also a major surgery that carries potential risks, such as the chances of organ rejection. That is why one needs to gather as much information as possible on organ transplants, before deciding to go for it.
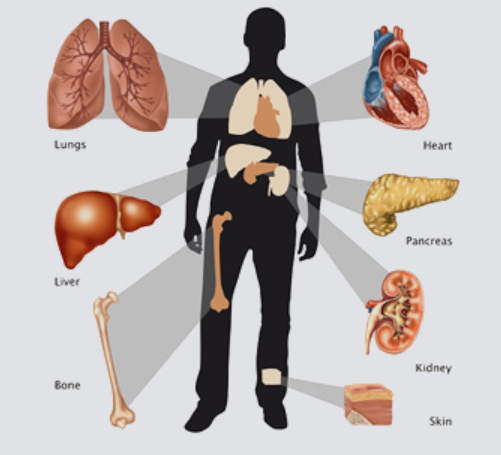
Different types of Organ transplantation in India
Different types of transplantations are listed below:
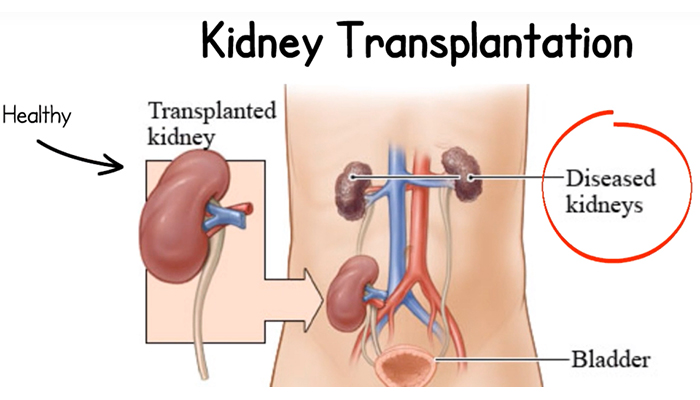
Kidney transplantation is a surgical procedure that’s done to treat kidney failure. The kidneys filter waste from the blood and remove it from the body through urine. They also help maintain the body’s fluid and electrolyte balance.
If kidneys stop working, waste builds up in the body and results in various issues.
People whose kidneys have failed usually undergo dialysis, which mechanically filters waste that builds up in the bloodstream when the kidneys stop working.
To know more about the Kidney transplant,
In a Liver transplant patient’s diseased liver is replaced with a healthy liver graft from a donor. Donor liver graft can be obtained from cadaver donors, or a family member may choose to donate a portion of his liver to the patient.
To know more about Liver transplants
In heart transplantation, a healthy heart from a cadaver donor who has suffered brain death is used to replace a patient’s damaged or diseased heart.
Due to the complexity of this procedure, strict medical criteria are imposed in assessing whether a donor’s heart is suitable for transplant and whether a potential recipient is suitable to receive the transplant.
 In Lung Transplantation One lung or both lungs from a cadaver donor are used to replace a patient’s diseased lung or lungs.
In Lung Transplantation One lung or both lungs from a cadaver donor are used to replace a patient’s diseased lung or lungs.
This type of transplant is commonly done on type 1 diabetic patients whose pancreas doesn’t work properly.
In Cornea Transplant damaged or cloudy cornea can be replaced surgically with a healthy, normal cornea, donated by another individual. It helps restore vision to those blinded by corneal disease.
Step-wise Process for Undergoing Organ Transplantation in India
Laws and Rules Governing Organ Transplantation in India
Transplantation of Human Organs Act (THO) passed in 1994, is the primary legislation related to organ donation and transplantation in India. This Act is aimed at regulation of removal, storage, and transplantation of human organs for therapeutic purposes and to prevent commercial dealings in human organs.
The amendment to the Act was passed by the parliament in 2011, and the rules were notified in 2014.
The essence of this legislation are :
- To accept brain death also as a definition of death
- To stop commercial dealing in organs
- To define the first relative (father, mother, brother, sister, son, daughter, and wife) who could donate organs without permission from the government
The main provisions of the Act (including the amendments and rules of 2014) are as follows:
- Brain death is identified as a form of death
- Allows transplantation of human organs and tissues from living donors and cadavers (after cardiac or brain death)
- Swap Transplantation: When a near relative living donor is medically incompatible with the recipient, the pair is permitted to do a swap transplant with another related unmatched donor/recipient pair.
- Organ retrieval is permitted from any hospital with an ICU facility once registered with the appropriate authority. Any hospital having Intensive Care Unit (ICU) facilities along with manpower, infrastructure, and equipment as required to diagnose and maintain the brain-stem dead person and to retrieve and transport organs and tissues including the facility for their temporary storage, can register as a retrieval center.
- The cost of donor management, retrieval, transportation, and preservation is to be borne by the recipient, institution, government, NGO, or society, and not by the donor family.
- Procedure for organ donation in medico-legal cases is defined to avoid jeopardizing determination of the cause of death and delay in retrieval of organs.
- Manpower and Facilities required for registration of a hospital as a transplant center are outlined.
- Infrastructure, equipment requirements and guidelines, and standard operating procedures for tissue banks are outlined.
- Qualifications of transplant surgeons, cornea, and tissue retrieval technicians are defined.
- Appointment of transplant coordinators (with defined qualifications) made mandatory in all transplant centers.
- Non-governmental organizations, registered societies, and trusts working in the field of organ or tissue removal, storage, or transplantation will require registration.
- The central government to establish a National Human Organs and Tissues Removal and Storage Network i.e. NOTTO (National Organ & Tissue Transplant Organisation), ROTTO (Regional Organ & Tissue Transplant Organisation), and SOTTO (State Organ &Tissue Transplant Organisation). The manner of establishing National or Regional or State Human Organs and Tissues Removal and Storage Networks and their functions are clearly stated.
- The central government shall maintain a registry of the donors and recipients of human organs and tissues.
- Penalties for removal of organs without authority, making or receiving payment for supplying human organs, or contravening any other provisions of the Act have been made very stringent in order to serve as a deterrent for such activities.
Estimate Cost for different types of Organ Transplantations in India
| Sr.No. | Name of Procedure | Cost in India (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kidney Transplantation | 13000 – 17000 |
| 2 | Liver Transplantation | 26000 – 33000 |
| 3 | Heart Transplantation | 40000 – 50000 |
| 4 | Lung Transplantation | 35000 – 45000 |
Frequently Asked Questions and patient concerns
1. How are organs from cadaver donors distributed?
Generally, donated organs are matched with individuals on an organ waiting list. Matching is based on a variety of factors including blood and tissue types, medical need, length of time on the waiting list, and weight of donor and recipient.
2. How long does the donor remain hospitalized?
After their surgery, the donor will typically remain in the hospital for four to seven days.
3. How long before the liver donor is fully recovered?
On average, most donors are fully recovered after three to six weeks. However, every donor’s recovery time is different.
4. Does becoming an organ donor mean that I won’t be eligible to receive the best medical care possible?
Your decision to donate an organ has no effect on the quality of medical care you can receive.
5. How long before the living donor recipient is fully recovered?
On average, most recipients are fully recovered after 3 to 6 months. However, this will depend on the severity of their condition, their age, and their general health.
6. What kind of lifestyle changes do you need to make after organ donation?
The only other lifestyle change we encourage is for transplant patients not to be involved in contact sports. We recommend that you stay active, avoid smoking and alcohol, and stick to a healthy diet.
7. Who can be the donor for transplantation?
There are two sources: cadaveric and living donors.
Cadaveric donors are individuals whose organs have been made available after brain death. As few cadaveric donations take place in India, living related liver transplantation is the only feasible option in our country. For living related transplants, a relative (usually parents) with a compatible blood type donates a portion of their liver to the child. Fortunately, the liver of the donor is able to grow back to full size in 812 weeks.
Living liver donors should be healthy adults, with a near normal body mass index (not obese) who have the ability to understand the procedure. The donor should have no medical, emotional, or psychological condition that could potentially increase the risk of this surgery.
8. What are the risks of transplant surgery?
There are risks with transplant surgery just as with any major surgery. Some immediate complications can include bleeding and blood clotting problems, respiratory problems, and malfunction of the donor’s liver. Long-term complications include rejection (when the child’s immune system does not accept the new liver) and infection. Fortunately, most of these complications are treatable.

MedicoExperts is a Global virtual hospital which is established to offer quality healthcare services at affordable pricing without compromising the success rates of the treatment.
MedicoExperts is having a network of highly experienced super specialist doctors and well equipped hospitals across the globe and offering second opinion through online video consultation and surgical interventions through its empanelled super specialist doctors at its network hospitals in 17 countries from 3 continents.
By the virtue of its approach and model, MedicoExperts is successfully achieve to deliver
- Latest and most advanced treatments with success rates of international benchmarks.
- Multiple cost options depending upon the hospital facilities, with the same doctor.
- Treatment option in multiple cities/state/countries.
- Trust and peace of mind.
Most suitable for patients who are looking for:-
- Planned Surgeries and treatment from most experienced doctors and at multiple cost options as per hospital facilities with best possible outcomes.
- Second Opinion from expert doctors.
- Complex cases involving multi specialities
- International patients looking for treatment from Indian doctors

Author Bio:
Dr. Subhamoy Mukherjee – Ph.D. (Oncology)
Dr. Subhamoy Mukherjee is a molecular oncologist with experience of working with genomic profiles. He has several years of experience in scientific writing. He takes strong interest in making people aware of different treatment approches in cancer, acute and chronic diseases. He also has interest in innovative approches for treating different mental and physical illnesses.
Content Medically Reviewed By MedicoExperts Editorial & Clinically Review Board