Oral cancer is a serious condition that can spread quickly if left untreated.
Early detection and prompt treatment are vital to stop its progression and improve survival chances.
Many people wonder, “How long does oral cancer take to spread?”
The timeline varies based on the type, location, and stage of the cancer. This article provides a detailed overview to help you understand the spread, symptoms, and effective treatments for oral cancer.
Even though this condition is quite serious, is oral cancer curable in India? Approximately 63% of patients who are diagnosed with oral cavity cancer manage to survive for at least five years after their diagnosis.
In the past, the mortality rate linked to this type of cancer has been alarmingly high. The reason for this is not that it is difficult to detect or diagnose, but rather that it is detected late in the disease process.
Let’s learn about the oral cancer timeline and its stages in detail:
How Long Does Oral Cancer Take to Spread?
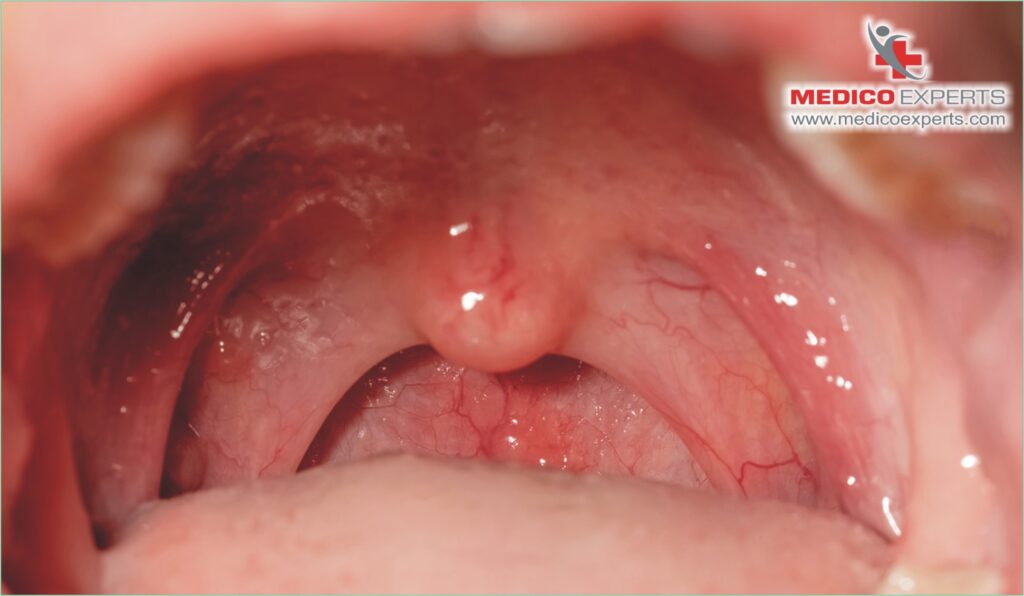
Oral cancer develops differently from person to person. In some, it spreads quickly, while in others, it spreads more slowly. Is oral cancer curable? The answer to this depends on the type of oral cancer, the location of the tumor, and the stage at which treatment begins are key elements that determine how quickly it spreads.
Factors Influencing Spread
1. Types of Oral Cancer:
More than 90% of oral cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. It begins in thin, flat cells called squamous cells.
Oral Squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) can spread quickly to nearby or distant parts of the body. According to a 2021 review, about 3-7% of OSCCs spread to secondary locations each year.
A 2017 study found that oral squamous cell carcinoma can spread to local, regional, or distant areas within 10-12 months after treatment of the primary tumor. In certain cases, it has the potential to spread as early as three months. Certain oral squamous cell carcinomas, like verrucous carcinomas, have slow growth rates and are not highly metastatic.
Other types of mouth cancer include:
- Lymphoma: Follicular lymphoma (FL) is the second most common type that slowly grows within the lymph nodes. Over a span of 6 to 12 months, the size of the lymph nodes affected by FL will double. It is not uncommon for patients to receive a diagnosis of FL one year or even longer after initially observing swollen lymph nodes.
- Sarcoma: Within a matter of weeks or months, high-grade sarcomas have a higher tendency to rapidly progress.
- Salivary Gland Cancer: Several types of salivary gland cancer grow at different rates and can affect any salivary gland.
- Mucosal Melanoma: They can become life-threatening in as little as 6 weeks. If not treated it can further spread to other parts of the body. Melanomas can occur on skin that is not normally exposed to the sun. In contrast to regular melanoma, nodular melanoma is highly dangerous.
2. Location of Cancer:
The primary location of oral cancer also affects the likelihood of its spreading. For example, a 2016 study found that about 1 in 15 gum cancers spread to distant areas compared to 1 in 25 tongue cancers.
Lip cancer, the most common type of oral cancer, spreads to nearby lymph nodes in 3-29% of cases, but distant spread is rare.
3. Stage of Diagnosis:
Early-stage oral cancer (Stages 1 & 2) is less likely to spread and has higher treatment success rates.
Advanced stages (3 & 4) are more aggressive and may spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs or liver.
The Typical Time It Takes Oral Cancer To Spread
The rate at which oral cancer progresses can vary significantly and depends on a number of factors, such as those mentioned above, the characteristics and aggressiveness of the tumor, the stage it is in, and the patient’s general health.
Due to these variations, it becomes challenging to identify a specific period over which oral cancer might spread. It’s important to find oral cancer early because finding cancer early greatly improves the chances of a better treatment outcome and stops it from spreading to other parts of the body.
There are ways you can detect oral cancer in its early stages and thus improve the outcome.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
How risky is mouth cancer? Oral cancer may have risks attached to it.
Multiple elements can contribute to an increased risk of developing oral cancer. Being aware of these risk factors plays a major role in early detection and prevention efforts. Here are some common ones:
1. Use of Tobacco
Using tobacco, in any form— smoking cigars or cigarettes and even pipe smoking, or the use of chewing tobacco is one of the major risk factors for oral cancer.
There are cancer-causing agents in tobacco that can harm your mouth cells’ structural makeup together with throat linings which would then lead to eventual changes turning into cancerous growths over time.
2. HPV infection
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, especially HPV type 16, is a known risk factor for oropharyngeal cancer, which affects parts of the throat, base of the tongue, and tonsils.
Cell changes caused by HPV have the potential to develop into cancer.
3. Excessive alcohol consumption
Regular, heavy alcohol consumption can irritate cells in the mouth and throat, making them more susceptible to cancer.
Alcohol also increases the harmful effects of tobacco, further increasing your risk.
4. Other risk factors
Apart from the above-mentioned risk factors, the following are some more you should consider, which include:
- Poor oral hygiene: Poor dental care and hygiene can lead to chronic infection and inflammation, increasing your risk of cancer.
- Diet: A diet low in fruits and vegetables may increase your risk of oral cancer because these foods contain antioxidants and other compounds that help protect cells.
- Age and gender: Oral cancer is more common in people over 40 and is more common in men than women.
- Sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun increases your risk of lip cancer because UV radiation damages the skin cells on your lips.
Is oral cancer deadly? Yes, but you can reduce your risk of oral cancer by understanding these risk factors and taking preventive measures.
Common Symptoms of Oral Cancer
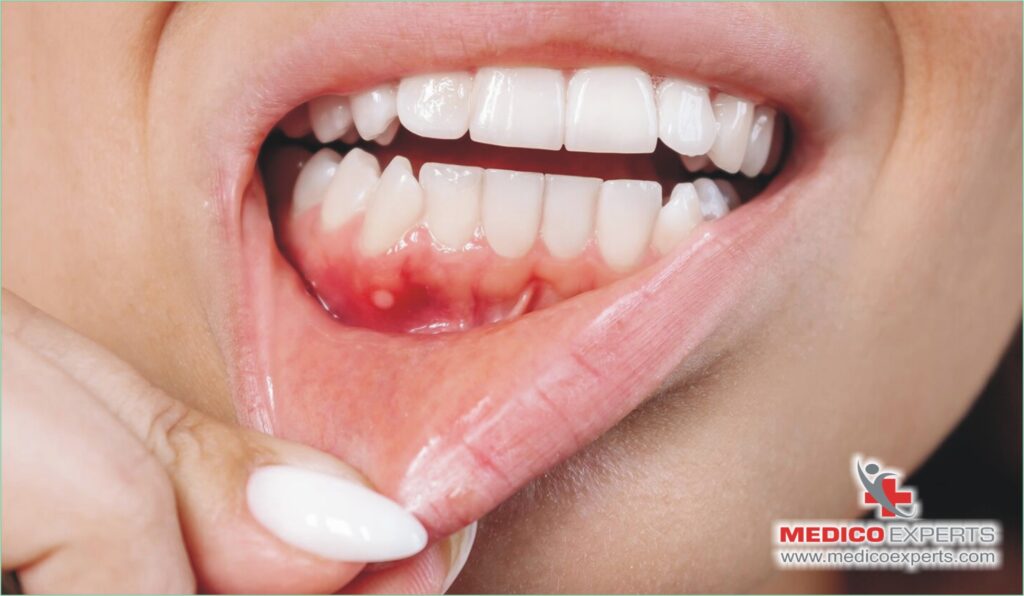
There are various symptoms linked with mouth cancer.
But these symptoms could often get you confused with general problems or changes in the mouth. For instance, some spots in your mouth that you can’t scrape away. These spots may be precancerous.
All the following conditions appear as patches in your mouth and throat, but each has a different color:
- Leukoplakia is flat white or grey patches in the mouth or throat.
- Erythroplakia describes red patches which are slightly elevated or flat. In cases of these patches, bleeding may occur upon scraping.
- Erythroleukoplakia presents patches that are both red and white in color.
Identifying the symptoms of oral cancer is crucial:
- Persistent Sores: Unhealed sores in the mouth or on the lips.
- White or Red Patches: Leukoplakia (white patches) or erythroplakia (red patches) that do not resolve.
- Unexplained Bleeding: Frequent bleeding in the mouth without a clear cause.
- Difficulty Chewing or Swallowing: Pain or discomfort when eating or speaking.
- Numbness or Pain: Tingling sensations or persistent pain in the mouth, face, or neck.
- Lumps or Thickened Areas: Growths or lumps in the cheek, tongue, or throat.
- Chronic Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath despite oral hygiene.
- Voice Changes: Hoarseness or changes in voice tone.
Stages of Oral Cancer
The stage describes how far the cancer has spread or advanced. Determining the stage of oral cancer helps your doctor explain to you the extent of the cancer.
Your doctor will determine the stage of your oral cancer by conducting a physical examination and analyzing the results of a biopsy or imaging test of oral tissue.
Adjustments to the stage can be made in the case of additional tests or surgery.
Stages of oral cancer:
Stage 0 Oral Cancer
Stage 0, also called carcinoma in situ, is the beginning of this stage. It describes abnormal cells in the lip or lining of the mouth that may develop into cancer.
Stage 1 Oral Cancer
Stage 1 represents the initial phases of cancer development. The tumor is no larger than 2 centimeters and the cancer has not yet reached the lymph nodes.
Stage 2 Oral Cancer
Stage 2 indicates the presence of a tumor that falls between 2 and 4 centimeters in size. In Stage II, the cancer has not yet reached the lymph nodes.
Stage 3 Oral Cancer
Stage 3 oral cancer describes cancer that is larger than 4 centimeters or has spread to lymph nodes in the neck.
Stage 4 Oral Cancer
Stage IV represents the most advanced stage of oral cancer. The size of the growth can vary, and it may extend to surrounding tissues, including the jaw or other areas within the mouth.
Stage IV oral cancer can be detected during the initial diagnosis. Stage IV oral cancer may also be recurrent oral cancer (cancer that comes back after treatment).
Note: The cancer may come back in 2 forms:
Regional Recurrence – where it first appeared in this case the lymph nodes or
Distant Recurrence – in other parts of the body.
Stage 3 and 4 cancers are more likely to come back than early-stage cancers.
Diagnosis of Oral Cancer
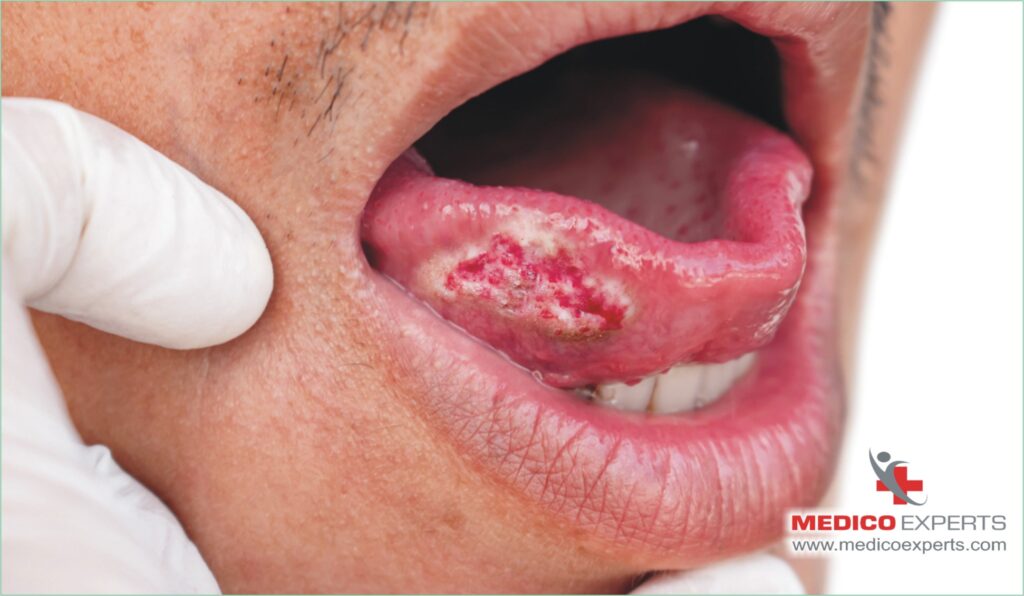
Is oral cancer curable if caught early? The signs of oral cancer could be detected by your dentist during regular dental check-ups. In case such signs are identified, the dentist might perform initial tests or refer you to a specialist in oral and maxillofacial surgery or head and neck surgery— commonly known as ENT specialists.
The tests done for oral cancer involve different approaches and examinations.
The inspection involves looking at your oral cavity, as well as feeling around the area. Moreover, the head, face, and neck are evaluated by your healthcare provider for signs of pre-cancer or cancer.
There are two types of biopsies:
Brush Biopsy
Brush biopsy is also termed a scrape biopsy or exfoliative cytology. In a brush biopsy, the area of concern is delicately scraped. This is done by using a small brush or spatula to collect cells that will be analyzed for signs of cancer.
Incisional Biopsy
An incisional biopsy involves the removal of small tissue samples by your healthcare provider to obtain cells for examination and cancer detection.
Indirect and Direct Pharyngoscopy and Laryngoscopy
There are two different techniques used to check the throat and larynx.
In Indirect pharyngoscopy and laryngoscopy: A small mirror is attached to a long and slim handle. This allows us to capture and visualize the base of the tongue, throat, and larynx.
Direct (flexible) pharyngoscopy and laryngoscopy: A thin and flexible tube with a light source is used. This viewing lens can reach places not easily seen by mirrors, offering a more complete view.
When found at an early stage, mouth cancer can be cured completely.
Treatment Options for Oral Cancer
Treatment options are influenced by several factors such as the type of oral cancer diagnosed, age, and health condition.
a. Surgical treatments for oral cancer
Surgery for the primary tumor: The tumors are either removed through the mouth or by making an incision in the neck area.
1. Glossectomy:
This is a surgical procedure involving partial or complete removal of the tongue.
2. Mandibulectomy:
Mandibulectomy is a surgical procedure for oral cancer involving the jawbone. It can also be described as a Maxillectomy. This involves removing part or all of the hard palate which is the bony roof of the mouth.
3. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy:
Another test that can help to understand whether cancer has spread beyond the original oral cancer is a Sentinel lymph node biopsy. Neck dissection would involve surgery to remove lymph nodes from your neck.
4. Reconstruction
A procedure that follows surgery that removes significant portions of tissue — may be performed to restore the missing areas after the tumor or to substitute a portion of your lips, tongue, palate or jaw. Reconstruction is done by taking healthy bone and tissue from other parts of your body.
But can mouth cancer be cured without surgery? Yes.
There are multiple treatment options to effectively address oral cancer. These are surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Doctors may consider a more forward-thinking approach by combining surgery with the following complementary treatments:
b. Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy uses powerful beams of energy to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. The team of experts may combine radiation therapy with other treatments.
c. Targeted Therapy:
This cancer treatment utilizes drugs or other elements to detect and target only the particular cancer cells thus limiting normal cells. Monoclonal antibodies refer to immune system proteins created in labs, they form the basis of cancer treatment strategies.
d. Chemotherapy:
Your doctor might give you cancer drugs that target and eliminate cancer cells, utilizing treatments that have a systemic impact on your body.
e. Immunotherapy:
An incredibly effective approach to combatting cancer, as it utilizes the immune system of the body to fight the disease. This form of treatment is often referred to as biological therapy.
Tumor Board Approach for Treating Oral Cancer
The MedicoExpert’s Tumor Board approach is headed by specialists like oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and pathologists who form a professional team for each oral cancer patient.
Our team holds periodic meetings to go through each case keenly, evaluating all possible courses of action that can be taken into consideration alongside the recent findings from research to come up with informed decisions on how best to take care of our patients.
Benefits of the Tumor Board Approach
MedicoExperts tumor board is a team of highly qualified experts to treat cancer patients. The MecioExperts Tumor can provide several benefits some of which are as follows:
Personalized Care: Every patient is offered a personalized treatment plan based on their own specific needs and depending on their unique medical background and the characteristics of the tumor.
Collaboration: An inter-disciplinary team ensures that all members collaborate to pool their knowledge and expertise to deliver care from different perspectives.
Specialization: Continuous monitoring, regular meetings, and follow-ups help our team to closely watch the progress of the patient and make appropriate modifications to the treatment plan.
Recommendations for Patients Concerned About Oral Cancer
Worried about oral cancer? How do you deal with oral cancer?
Below are simple steps that can lower your risk and ensure early detection:
Stay away from Tobacco: Abstain from smoking and using tobacco so as to lower your chances of developing cancer.
Being mindful: Limit your alcohol consumption. Excessive drinking can further increase risks especially when coupled with tobacco use. Pay attention to your oral cavity and any unusual sores, lumps or changes that occur.
Be cautious against HPV: Consider vaccination against human papillomavirus (HPV), which plays a major role in oral cancer.
Listen to your body: If symptoms persist seek medical attention for instance severe difficulty swallowing.
Takeaway

Oral cancer spreads over a wide range of timeframes. It is important to consider the patient’s health along with tumor type and stage.
Early detection and treatment are critical to improving outcomes and preventing the cancer from spreading to other parts of the body. Regular dental checkups play a vital role in early diagnosis.
The Tumor Board approach provides personalized and collaborative treatment plans. These plans are crafted to improve the patient’s care and treatment outcomes.
If you have concerns about oral cancer, schedule a consultation with Medicoexperts’s oral cancer specialist.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. At what age does oral cancer typically occur?
A: Individuals over the age of 40 are more prone to developing oral cancer.
Q2. I’m worried about oral cancer. How often should I get screened by a dentist?
A: It is recommended that you have a dental checkup every six months, especially if you have risk factors such as smoking or HPV.
Q3. How long can you live with oral cancer?
A: The five-year survival rate for oral cancer is about 63%. Based on the the cancer stage and its respective treatment it can differ.
Q4. If I have oral cancer, will it definitely spread?
A: Not necessarily. The spread of oral cancer depends on factors in particular the type and stage of the cancer. Early detection and treatment can help prevent the spread.
Q5. What are some of the latest advancements in oral cancer treatment?
A: Recent advances include tumor board approaches, targeted drug therapy, and immunotherapy. MedicoExperts Tumor Board has a team of experts that provides customized care and improves treatment outcomes.
Q6. How can I get an appointment with tumor board for treating oral cancer?
To make an appointment with a tumor board for oral cancer treatment contact a specialized cancer treatment center. You can also contact MedicoExperts for help scheduling an appointment with our tumor board team.
References
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/11184-oral-cancer
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7566351/
- https://oralcancerfoundation.org/facts/
- https://oralcancerfoundation.org/understanding/hpv/
- https://cancersurgeon.co.in/blog/how-long-does-oral-cancer-take-to-spread/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/oral-cancer/how-long-does-oral-cancer-take-to-spread#symptoms
- https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/types/mouth/mouth-cancer-diagnosis/mouth-cancer-stages
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4981925/
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/fullarticle/2594265
- https://www.cancercenter.com/cancer-types/oral-cancer/treatments/surgery
- https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/health-concerns/tobacco/legislation/tobacco-product-labelling/smoking-oral-cancer.html
Recommended Articles For You
Oral cancer is one of the most common cancer types that is becoming a growing problem in many parts of the…..Read More
Ready to witness the remarkable shift in the lives of those touched by gastrojejunostomy? Gastrojejunostomy, often…..Read More
Recommendations To Understand Different Treatments
Do you know you can train your immune system to fight even cancer cells with Immunotherapy in India? The treatments of…..Read More
Do you know, that you can increase the lifespan of cancer patients by targeted therapy while significantly reducing the…..Read More
Medically Reviewed By MedicoExperts Editorial & Clinical Review Board
Medical Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and not medical advice. Consult a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.



