Advanced & Patient-Centric Brain Tumor Treatment In India
Do you have apprehensions related to brain tumor removal procedures and the side effects related to them?
You want faster recovery and a hassle-free treatment process. Brain tumor treatment in India is one way to make sure that your treatment journey is smooth and that you recover faster.
Brain tumors can be aggressive and the condition may deteriorate fast if the tumor is not detected and treated early.
So, early detection and treatment are important to live a tumor-free healthy life.
Hence without wasting any more time, let’s learn what a brain tumor is and how coming to India can help you treat it effectively.

What is Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of the cells present in the brain that is uncontrollable.
The brain tumors can be:
- Benign or non-cancerous
- Malignant or cancerous
Apart from being cancerous and non-cancerous brain tumors can be:
Primary tumor: Primary brain tumors originate in the brain or the central nervous system.
Secondary brain tumors or metastatic brain tumors: This type of brain tumor develops when cancer from other parts of the body like the lungs, and esophagus spreads to the brain.
What are the different types of Brain Tumors?
There are around 120 types of brain tumors and some of the most common types of brain tumors are called gliomas. Gliomas arise from glial cells and the glial cells support the function of the neurons.
Gliomas can be categorized as Astrocytoma, Oligodendroglioma, Ependymoma, and Glioblastoma.
Astrocytoma originates from cells known as astrocytes which are branch-like structure that supports nerve cells. The different types are Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma, which falls under Grade 1, Low-Grade Astrocytoma, and Anaplastic Astrocytoma.
- Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma (JPA) develops in the cerebrum, optic nerve tracts, the brainstem, and the cerebellum. (parts of the brain)
- It is common in children and adolescents.
- Low-grade astrocytomas are slow-growing.
- Very few cases spread to other parts of the CNS.
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma progresses and invades more rapidly than low-grade astrocytomas.
- Tumor cells are not all the same in their appearance either.
- It Invades neighboring tissue.
- It is prevalent in both men and women of the age bracket 30-50 years.
It originates in the glial cells known as oligodendrocytes.
- Oligodendroglioma is seen mainly in the frontal or the temporal lobe (parts of the brain).
- It can be categorized as low grade or high grade.
- Prevalent in young adults and middle-aged men and women, but it can also be present in children.
Ependymoma develops from the cells that form the lining of the passages that carry cerebrospinal fluid.
- It can be either cancerous or noncancerous.
- The cancerous type can invade the neighbouring tissues and can press on the nerves.
Glioblastoma multiforme is the most aggressive and most frequent of the malignant primary brain tumors in the adult and belongs to the category of gliomas.
Categorized as grade 4 astrocytoma which is the most aggressive form, GBM arises from a type of cells known as glia.
GBM occurs mainly in the cerebral hemispheres (parts of the brain) but can occur anywhere in the brain or brainstem (part of the brain) or the spinal cord.
- It is often made up of one or more than one type of cell.
- It may arise from lower-grade astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma
- More frequent in the elderly and men than in women
- It is, however, less frequent in children.
The other types of brain tumors apart from gliomas are CNS Lymphoma, Craniopharyngioma, Medulloblastoma, Primitive Neuroectodermal, and Acoustic Neuroma.
CNS Lymphoma is a type of cancer that develops in the lymphatic system in the brain.
- CNS Lymphoma is very aggressive.
- Usually, it involves multiple tumors throughout the central nervous system (CNS).
- It is more common in people whose immune systems are compromised.
- It often develops in the brain, commonly in the areas adjacent to the ventricles (parts of the brain).
It is most common in the parasellar region, an area at the base of the brain and near the optic nerves.
- Craniopharyngioma tends to be low-grade.
- It is often accompanied by a cyst.
It is often located in the cerebellum or near the brain stem (parts of the brain).
- Medulloblastoma can spread to the spinal cord through the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- It can cause hydrocephalus (water on the brain).
- It occurs most often in children under the age of 10 but may occur in adults.
This category consists of several tumor types including Pineoblastoma, which affects the pineal gland, Medulloblastoma which afflicts the cerebellum and Cerebral Cortex (parts of the brain).
- Primitive Neuroectodermal is very hostile and tends to spread throughout the CNS.
- It develops from the basic structures of the brain cells.
Acoustic neuroma also goes by other names such as schwannoma, vestibular schwannoma, or neurilemmoma.
- Acoustic Neuroma occurs in cells that are involved in the covering for nerve fibers.
- Usually, it develops near the eighth cranial nerve(cranial nerves are those nerves that arise from the brain); however, it may develop closeby to any other cranial or spinal nerves.

What is the difference between Cancerous and Non-Cancerous Brain Tumors?
Brain tumor results from uncoordinated and uncontrolled growth of the brain cells. In some people with brain tumors, the abnormal cell growth is rapid, while in a few people, it is slow.
Generally, cancerous tumors multiply and spread rapidly, whereas, in non-cancerous tumors, the cell multiplies slowly. Non-cancerous tumors do not spread to other parts of the body.
Brain tumors need proper care and treatment, even if they are non-cancerous. By initiating timely treatment, you can avoid severe complications and damage caused to other areas of the brain and spine.
What are the symptoms of Brain Tumors?
Typically, brain and other nervous system tumors do not cause any symptoms. However, the overgrowing tissue presses the neighbouring nerve tissues. The symptoms of brain tumors are not the same for everyone, but it depends on the location of it. However, the common symptoms of brain tumor include:
- Morning headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures
- Difficulty in walking as the body loses its ability to balance
- One might experience vision, hearing, or speech problems or sometimes all three
- Loss of memory
- Changes in personality, mood, and focus
- Constant numbness or tingling sensation in the hands or legs
Who is at risk for developing Brain Tumors?
Anything that elevates your possibility of developing the disease is called a risk factor. The risk factors for brain tumors include:
- Prolonged exposure to X-ray or other harmful radiation
- Family history of cancer
- People with genetic syndromes like Von Hippel Lindau Disease
- People having cancer elsewhere in the body
What are the different grades of Brain Tumors?
The different grades of tumors show the extent of the spread and growth of the brain tumor. Broadly brain tumors are divided into four grades, i.e., from Grade 1 (the least aggressive) to Grade 4 (the most aggressive). The features of different grades of brain tumor are:
Grade I brain tumor:-
- Usually non-cancerous
- The growth of the brain tumor in this stage is slow
- Unlike in advanced grades, the change in the structure of the cells is minimal in grade 1 brain tumor
- Have good prognosis
Grade II brain tumor:-
- In this stage, the brain tumor grows at a relatively slow speed
- Cancer begins to spread in the neighboring structures
- Changes in the appearance of the tumor cells start to become evident
Grade III brain tumor:-
- The structure of the cells becomes abnormal
- The cells divide at a relatively high speed
- Tumor cells infiltrate the neighboring structures
Grade IV brain tumor:-
- Cancerous
- Very aggressive
- The brain tumor grows abnormally fast
- Spreads to other parts of the brain
- Abnormal structure of the cells
- New blood vessels form around the brain tumor to maintain its growth
- Necrosis or cell death begins to start in the tumor
What is Brain Tumor Staging?
Brain tumor staging helps to determine the extent of the spread of cancer. If the brain tumor is secondary, staging is essential as it lets the doctor know the extent of the spread of the tumor. However, for primary brain tumors staging is not required because primary brain tumors do not spread beyond the nervous system.
How is a Brain Tumor diagnosed?
If you are experiencing the symptoms of brain cancer, your doctor can suggest that you undergo a few tests to confirm the diagnosis.
During the physical examination, your doctor will check the reflexes of your body along with muscle strength. Along with that, your doctor will also check your vision, alertness, coordination, and balance.
If your doctor finds something amiss he can refer you to a neurologist for a detailed neurological examination.
With the help of imaging tests, your doctor can get a picture of your brain and spinal cord. Doctors usually prefer either a computer tomography (CT ) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to understand brain diseases. Sometimes your doctor can advise you to undergo a positron emission tomography (PET) scan. The PET scan helps your doctor to understand the difference between scar tissue and tumor tissues.
If your doctor finds a growth he may suggest you undergo a biopsy to ensure if the growth is cancerous or not. During the biopsy, they remove tumor tissues to study the cells.
Generally, doctors avoid fine needle biopsy for brain tumors as it is challenging. Open biopsy is mainly performed in cases of the primary tumor, where your doctor removes the tumor surgically while sending a few tumor tissues for biopsy.
Lumbar puncture is mainly used to detect cancer cells in the cerebrospinal fluid. Usually, lumbar puncture is considered to be a safe procedure. However, an MRI or CT scan must be performed before lumbar puncture.
Your doctor may advise you to do a routine blood test to keep a count of your blood cells. Also, they may advise you for a kidney and liver function test to ensure that the organs are functioning properly.
What are the best Brain Tumor Treatments available in India?
The following treatments are available for treating brain tumors:
Surgery is considered the best brain tumor treatment approach for removing the tumor cells. Surgery alone or combined with radiation therapy helps control many types of tumors. It also helps in relieving symptoms of brain tumors.
However, surgery may not be indicated in certain types of brain tumors like lymphomas.
While it can efficiently remove tumors, there are chances that one may develop a few complications like bleeding, infection, seizure, or swelling of the brain.
But there is nothing to worry about, as these complications can be managed easily by medication and proper care.
Different Types of Brain Tumor Surgery
Craniotomy is one of the types of brain tumor surgery. It is the process of making a hole in the skull to remove all or most of the tumor. The surgeon then detaches the tumor, puts the bone back in its place, and then uses small metal brackets and stitches to fix it.
A craniotomy is performed with the patient under general anesthesia, therefore the patient will be asleep and unconscious and will not be able to feel any pain.
A surgeon may use a scalpel, special scissors, or ultrasound to cut the tumor and then uses a suction device known as the ultrasonic aspiration to remove the tumor.
Besides these, they may use different tools for the procedure, including:
A Fluorescent Dye:
a patient will ingest this, and it helps in the identification of tumor cells. Doctors use this in combination with a special microscope to distinguish between normal and abnormal cells.
Cortical Mapping:
It enables doctors to determine the parts of the brain that are involved in critical activities like movement, speech, and feeling. It also provides the surgeon with a map of the tumor’s location for better results.
Awake Craniotomy:
This is the same as a craniotomy, only a patient is not put to sleep during the operation. A doctor might recommend this surgery if the tumor is located in the areas of the brain that regulate vital functions of the body, for instance, speech, sense, or movement.
At the beginning of the operation, a patient will receive a general anesthetic, which a doctor will then decrease so that the patient stays awake. The surgeon might also request a person to perform activities during the surgery to assess the working of various organs.
Neuroendoscopy or keyhole brain surgery is an operation that is done to get rid of all or a portion of tumors located in the ventricles of the brain which are the hollow chambers that contain cerebrospinal fluid.
A surgeon employs an endoscope which is a long flexible tube with a viewing lens at the tip, and a view screen.
It requires drilling a small opening on the head known as the burr hole to enable the insertion of the endoscope. The malignant tissue is removed from the brain via the endoscope with the help of small forceps held by the surgeon.
Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy:
Laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) is a relatively new surgical procedure used in the management of brain lesions. It employs light energy to produce a heat effect on the targeted tissue to destroy the lesion.
Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery:
This is a form of surgery used in cases of tumors in the base of the skull. This is where a surgeon places an endoscope into the nose and accesses the lower area of the brain.
Radiation therapy is considered one of the best brain tumor treatment approaches for killing leftover tumor cells after surgery. It is useful for treating brain tumors in people who cannot undergo surgery and are not responding well to the medicine.
During radiation therapy, the tumor cells are treated by radiation beams. The high-intensity beams kill the cancerous cells.
Many people complain of headaches, nausea, and vomiting after it . Usually, people get tired and irritable after the radiation therapy session. Some people complain of hair fall after it.
During chemotherapy, your doctor will administer anti-cancer pills orally or through an IV line.
Although chemotherapy works well for different cancers, it is usually not advised for treating brain tumors because the drugs administered through chemotherapy sometimes do not reach the brain.
However, if the drugs are injected directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, chemotherapy can work efficiently.
Recovery from Brain Tumor Surgery/Treatment
The recovery plan will be designed according to your needs after your brain surgery.
Besides complete recovery from surgery, there is special neurorehabilitation that includes physical, speech, and occupational therapy to help you get the most favorable outcome after the surgery for a brain tumor.
Rehabilitation is quite crucial in the healing process since it enhances the quality of life after the surgery for a brain tumor.
Physiotherapists and occupational therapists will assist you to regain strength, movement, and ability to perform everyday tasks by encouraging you to practice exercises.
The behavioral changes are problematic and are likely to place you and your family under stress. Therefore, the activity of cognitive rehabilitation will assess the work of memory, focus, and other cognitive capacities, while counseling or psychotherapy will handle the emotional component of the case.

What is the success rate of Brain Tumor Treatment in India?
The survival rate or the success rate shows the portion of people who will survive for the next five years after getting diagnosed with a brain tumor.
The five-year survival rate among people with brain tumors is approximately 79%-35% based on the age, stage, type, and location of the cancer.
Detailed Survival According to Types
Oligodendroglioma – 90% for patients aged 20-44, 82% for patients aged 45-54, and 69% for patients 55-64 of age.
Meningioma – 84% for patients aged 20-44, 79% for patients aged 45-54, and 74% for patients having 55-64 of age.
Glioblastoma – 22% for patients aged 20-44, 9% for patients between 45-54, and 6% for patients aged 55-64.
Anaplastic astrocytoma – 58% for patients with ages between 20-44, 29% for patients with 45-54 years age and 15% for patients aged 55-64.
What is the cost of Brain Tumor Surgery in India?
The cost for brain tumor surgery in India ranges between USD 5000-9000 (INR 4,50,000-8,00,000) depending upon the surgeon and hospital.
The cost of radiotherapy for brain tumors in India ranges between USD 1,000- 2000 ( INR 90,000- 1,80,000 ) per sitting.
At the same time, the cost of chemotherapy for brain tumor treatment ranges between USD 300- 1200 (INR 27,000 – 1,08,000) per sitting.
However, the cost of treatment for brain tumors varies for every patient depending on their health, treatment involved, medication, location, and the stage of cancer.

How to choose the best Neurosurgeon for your Brain Tumor Treatment?
We know choosing the right neurosurgeon for your brain tumor surgery can sometimes be overwhelming.
We believe that an ideal neurosurgeon for your brain tumor surgery would be someone who not only has very good experience in terms of the number of years but also has handled thousands of cases with a success rate of more than 75%.
Additionally, you must ensure that the doctor is well-trained with the latest surgical techniques, equipment, and protocols.
How to choose the best hospital and country for Brain Tumor Surgery?
Brain tumor surgeries are complex surgeries that require advanced imaging techniques, innovative technologies, and well-trained staff.
The success of brain tumor surgery depends on the teamwork of the neurosurgeon, the surgical team, and the post-operative patient care team.
Although the UK and USA have the best neurosurgery hospitals, the treatment in Western countries may cost you a lot.
However, the cost of treatments and surgeries in India is just about 40 – 50% of the cost in the USA, the UK.
India has seen an upsurge in the number of people coming from other countries for their treatment. The reason for this upsurge in the numbers is that India houses a few of the world’s best neurosurgeons. Apart from well-trained neurosurgeons India also offers specialized and well-trained operative and post-operative care teams, along with world-class surgical and hospital infrastructure, that are capable of handling complex cases, at an affordable cost.
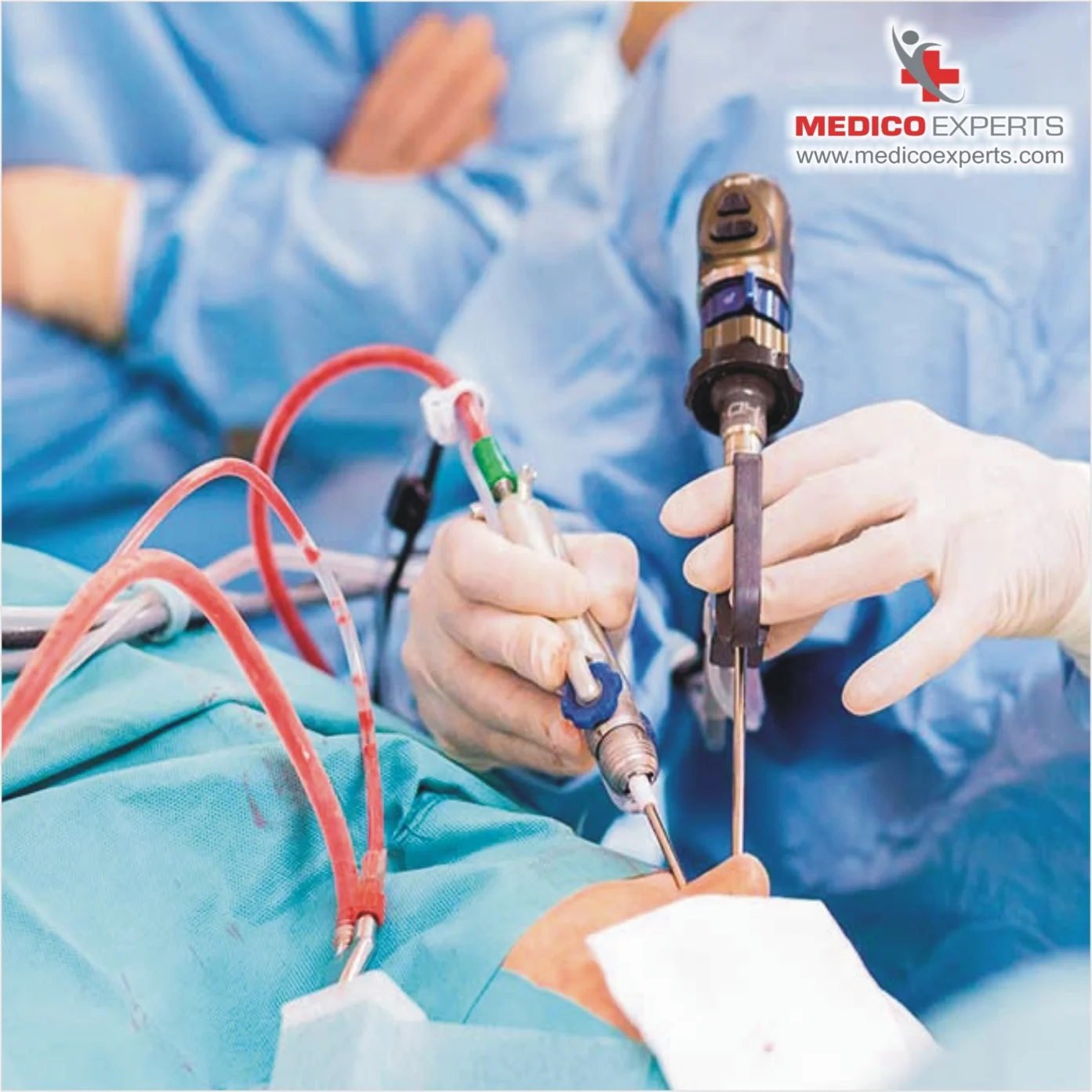
How do MedicoExperts assist International Patients in receiving quality low-cost Brain Tumor Surgery in India?
These are the ways MedicoExperts will help you when you come to India for treatment:
- Availability of best-in-class & ISO-certified Brain Tumour Surgery hospitals in India
- Instruct you to select doctors and get the right opinions from a dedicated Tumor Board
- Appropriate conversations with doctors
- The services are made at a convenient time for the client
- Reduce long waiting times
- Help in applying for and getting Medical Visas.
- Boasts of offering affordable and cheap medical packages for its clients.
- Pick-up & Drop facility
- Ensure that you have Boarding & Lodging facilities
- Check-in hotel services and patient safety services designed by professional personnel for the patients
- Complication-free admission to hospitals
- Food and lodging arrangements are made as per the client’s choice.
Takeaway
Certain types of brain tumors are really aggressive and require immediate intervention for recovery and survival.
While, there are different kinds of surgeries and other therapies available to tackle the problem, only the right doctors and a well-equipped team of healthcare professionals in a tumor board can lessen the various kinds of burdens of the patient and their families.
MedicoExperts has a dedicated tumor board that can help you make prompt decisions for faster treatment and cure. The tumor board will consist of specialists from neurosurgery and oncology as well as radiotherapy and reconstructive surgery. It is the combined effort of the members of the tumor board that will help in the fast resolution of medical problems and will result in the most effective treatment and care.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. How long can you live with a brain tumor without treatment?
Patients with aggressive glioblastoma live for an average of 4 months without treatment. However, it is not advised to live without treatment if you have a brain tumor.
Q2. How did I know I had a brain tumor?
The following can be the warning signs of a brain tumor:
- Stiffness in the temples accompanied by pain increasing in the morning.
- Headache, migraines, and other instances of headaches that occur at a closer interval and/or are more painful.
- Occasional headaches which are often termed tension head aces or migraines.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Visual disturbances like having a blurry sight or double, vision or even losing some part of vision, particularly on the peripheral part of the sight line.
- Paralysis of an arm or a leg.
- Trouble with balance.
- Speech problems.
- Feeling very tired.
Q3. Is awake craniotomy surgery common in India?
Lately, India has seen a surge in the number where people who opted for awake craniotomy surgery for their brain tumors. The innovative technology used by neurosurgeons ensures that you receive the best brain tumor treatment in India while keeping the cost of the treatment reasonable.
Q4. What is the treatment for brain tumors in India?
Based on the location, grade, and type of brain tumor your doctor will suggest you the best treatment for the brain tumor. Typically, there are various options that they choose for the treatment of brain tumors in India.
Surgery is the most common treatment method used by doctors to treat brain tumors. Apart from surgery, your doctor can suggest radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
Q5. What is a gamma knife?
The gamma knife is an innovative treatment approach for metastatic brain tumors. Gamma knife is an advanced radiation treatment method that helps to treat secondary brain tumors in adults and children.
Q6. Are there any side effects of brain tumor treatment?
The side effects of brain tumor treatment primarily depend on the treatment chosen.
A few people who underwent chemotherapy may experience the following side effects:
- Hair fall
- Mouth ulcers
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Bitterness in mouth
- Altered appetite
- Constantly dry mouth
A few people who underwent surgery may experience the following side effects of brain tumor surgery:
- Seizure
- Swelling in the brain
- Bleeding
Usually, people experience the following side effects after radiation therapy for brain tumor:
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Hair loss
- Altered taste
- Mouth ulcers
- Fatigue
Best Brain Tumor Surgery Hospitals in India

MedicoExperts is a Global virtual hospital which is established to offer quality healthcare services at affordable pricing without compromising the success rates of the treatment.
MedicoExperts is having a network of highly experienced super specialist doctors and well equipped hospitals across the globe and offering second opinion through online video consultation and surgical interventions through its empanelled super specialist doctors at its network hospitals in 17 countries from 3 continents.
By the virtue of its approach and model, MedicoExperts is successfully achieve to deliver
- Latest and most advanced treatments with success rates of international benchmarks.
- Multiple cost options depending upon the hospital facilities, with the same doctor.
- Treatment option in multiple cities/state/countries.
- Trust and peace of mind.
Most suitable for patients who are looking for:-
- Planned Surgeries and treatment from most experienced doctors and at multiple cost options as per hospital facilities with best possible outcomes.
- Second Opinion from expert doctors.
- Complex cases involving multi specialities
- International patients looking for treatment from Indian doctors
Relevant Articles For You
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441874/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2151783/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8328013/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10527911/
- https://journals.lww.com/rca/fulltext/2018/06002/awake_craniotomy__indications,_benefits,_and.9.aspx
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7023945/
- https://www.moffitt.org/cancers/brain-cancer/survival-rate/
Recommendations To Understand Different Treatments
Liver Cancer Treatment With Proton Beam Therapy
Cancer that originates in the liver is termed liver cancer. The liver is one of the largest organs of the body and it lies below the diaphragm and in the upper right quadrant of the…..Read More
Medically Reviewed by MedicoExperts Editorial & Clinical Review Board on 17 September 2024

Author Bio
Dr. Subhamoy Mukherjee is a molecular oncologist with experience working with genomic profiles. He has several years of experience in scientific writing. He takes a strong interest in making people aware of different treatment approaches in cancer, and acute and chronic diseases. He also has an interest in innovative approaches for treating different mental and physical illnesses. View all posts by Dr. Subhamoy Mukherjee



















